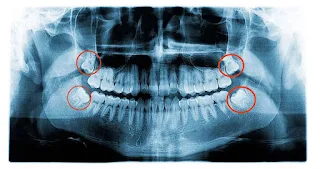
causes and signs and syptoms of impacted wisdom teeth
Impaction
A tooth that is incompletely or partially erupted is positioned against another tooth, bone, or soft tissue so that further eruption of the teeth is unlikely possible. The most common teeth which are impacted are wisdom teeth ( 3rd Molars) and Canines.
The following are the order of impacted teeth,
I) Mandibular third molars
II) Maxillary third molars
III) Maxillary cuspids
IV) Mandibular bicuspids
V) Mandibular cuspids
VI) Maxillary bicuspids
VII) Maxillary central incisor
VIII) Maxillary lateral incisor
Causes for Impaction of the tooth
Local Causes
• Irregularity in position and pressure of the adjacent tooth.
• Density of overlying and surrounding bone.
• Over-retained deciduous teeth.
• The ectopic position of the tooth bud.
• Lack of space due to the underdeveloped jaw.
• Any obstruction due to hard and soft tissue.
• Diaccleration-abnormal path of eruption due to traumatic force during eruption period.
Systemic Causes
A) Prenatal causes
1) Hereditary
B) Postnatal causes
1. Rickets
2. Anemia
3. Tuberculosis
4. Malnutrition
5. Endocrine abnormalities
6. Congenital syphilis
C) Rare Condition
1. Progeria
2. Oxycephaly
3. Osteopetrosis
4. Cleft palate
5. Cleidocranial dysplasia
Signs and Symptoms of Impacted Wisdom Teeth
• Pain is most common in wisdom teeth due to improper angulation of the tooth which forces the adjacent teeth. Sometimes it may be due to pericoronitis.
• Dental Caries are most commonly associated with the impacted teeth or their adjacent teeth.
• Patient has reduced mouth opening due to associated pericoronitis.
• The overlying soft tissue shows the four cardinal signs of inflammation such as redness, swelling, and warmth.
• Chills, fever, malaise, halitosis.
• Regional lymph node enlarged.
• Trismus may be present.
PERICORONITIS
Pericoronitis refers to the inflammation of soft tissue around and covering the impacted wisdom teeth ( 3rd Molars)
Causes for Pericoronitis
• Bacterial growth beneath the soft tissue covering the partially or completely erupted tooth.
• Due to the trauma in the overlying soft tissue.
• Supraerupted maxillary third molar on an opposing.
• Unerupted or partially erupted mandibular third molars (Wisdom teeth). The inflammation along with bacterial innovation may also cause pericoronitis.
Treatment for Pericoronitis
1. By Surgical removal of the Impacted Teeth (Permanent relief from pain)
2. By Conservative Treatment (For Temporary relief from pain)
Firstly, Clean the tooth with the ultrasonic scaler which removes the calculus and plaques beneath the covered flap, if present. Then, Irrigate with saline beneath the flap. 10cc syringe with 20 gauge needle can be bent slightly for better access. 1CC iodine
the solution can also be used to irrigate the flap. Some of the irrigating solutions are,
• Phenol 5 6cc
• 24cc
• Tincture of aconite, 12cc
• Tincture of 18cc
Irrigation is carried out until the subside and after this, the tooth can be extracted. if the tooth will erupt in a normal position and
helps in the overlying flap should be removed.
3. Surgical removal of the flap (Operculectomy)
The dense fibrous flap called the operculum covers half of the occlusal surface of the partially erupted third molar (Wisdom teeth The procedure for the removal of a flap is called an operculectomy. this flap is removed with a scalpel or electrosurgical scalpel, or radiosurgical loop.
ELECTROSURGICAL SCALPEL
In this, there is no need to apply the
pressure by using the usual scalpel, by using the electrosurgical scalpel, the tissue can be cut accurately and visibility is increased and
bleeding is reduced.
RADIOSURGICAL LOOP
The radiosurgical loop is placed beneath the flap as posteriorly as possible. Now passing the current through the loop results in the cutting of bulk tissue. When the flap is the tissue distal to the tooth is removed for proper eruption.
Indications for Wisdom Teeth Extraction
• In case of any symptomatic impacted tooth like food abscess, untreatable periapical pathology, cellulitis.
• Unrestorable caries. present in the wisdom teeth (3rd Molars).
• If there are any Periodontal diseases in an impacted they should be extracted as early as possible.
• In the case of dentigerous cyst formation.
• Buccoverted impacted third molar results in cheek bite, traumatic fibroma, or frictional keratosis.
• Orthodontic removal of the third molar is rarely indicated.
• In the case of mandibular fracture where a third molar is involved.
• Atypical pain in an unerupted third molar.
Contraindications for Wisdom Teeth Extraction
• Medical history contraindicates surgical procedure
• Very deep impacted tooth in subjects who don’t have any pathology or any symptoms to avoid damage to the vital structure.
• Impacted tooth which can erupt in a proper position and functionally effective
• Partially impacted tooth which can be used as an abutment in fixed partial denture
• The Third molar should not be removed in case of the patient have any surgical complications like a fracture of the atrophic mandible.










COMMENTS